Description
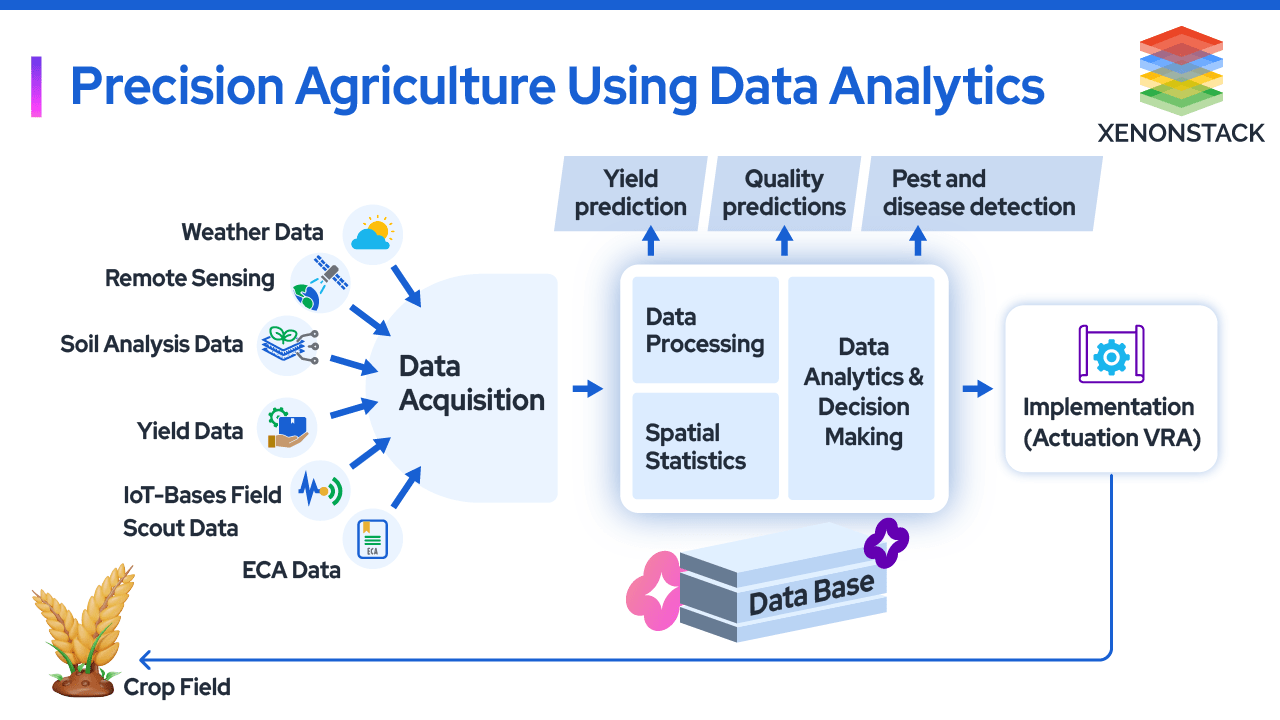
Data analytics is crucial in precision agriculture by leveraging large volumes of data collected from various sources to optimize farming practices. Here’s an overview of how data analytics is used in precision agriculture:
Data Sources in Precision Agriculture
- Field Sensors and IoT Devices
- Soil Moisture Sensors: Measure soil moisture levels to determine irrigation needs.
- Weather Stations: Monitor weather parameters such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation.
- Crop Health Sensors: Detect plant health indicators like chlorophyll levels and pest infestations.
- GPS and Satellite Imagery: Provide spatial data on field boundaries, crop growth stages, and yield variability.
- Farm Machinery and Equipment
- Precision Planters and Harvesters: Collect data on seed placement, plant spacing, and yield during harvest.
- Tractors with GPS: Enable precise application of inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides.
- Remote Sensing Technologies
- Satellite Imagery: Capture high-resolution images to monitor crop health, growth patterns, and field conditions.
- Drones: Conduct aerial surveys for detailed mapping, crop scouting, and monitoring hard-to-reach areas.
Types of Data Analytics in Precision Agriculture
- Descriptive Analytics
- Data Visualization: Use charts, graphs, and maps to visually represent historical data trends and patterns.
- Dashboard Tools: Provide real-time insights into crop conditions, soil moisture levels, and weather forecasts.
- Diagnostic Analytics
- Root Cause Analysis: Identify factors contributing to crop stress, yield variations, or pest outbreaks based on historical data.
- Performance Metrics: Evaluate the effectiveness of irrigation, fertilization, and pest management practices.
- Predictive Analytics
- Crop Yield Forecasting: Use historical data, weather forecasts, and soil conditions to predict crop yields and plan harvest schedules.
- Disease and Pest Outbreak Prediction: Analyze environmental factors and pest population dynamics to anticipate outbreaks and take preventive measures.
- Prescriptive Analytics
- Recommendation Systems: Provide actionable insights and recommendations for optimal irrigation scheduling, fertilizer application rates, and crop rotations.
- Decision Support Systems: Assist farmers in making informed decisions based on data-driven insights and predictive models.
Benefits of Data Analytics in Precision Agriculture
- Precision and Efficiency
- Optimized Resource Use: Tailor inputs such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides to specific crop and soil conditions, reducing waste.
- Timely Interventions: Respond quickly to changes in weather, soil moisture, and crop health to minimize risks and maximize yields.
- Sustainability
- Environmental Stewardship: Reduce environmental impact by minimizing chemical runoff, soil erosion, and water usage.
- Long-Term Soil Health: Enhance soil fertility and structure through precise nutrient management and conservation practices.
- Decision-Making Support
- Risk Management: Mitigate risks associated with weather variability, pests, and market fluctuations through data-driven insights.
- Financial Planning: Improve budgeting and forecasting by optimizing input costs and predicting crop yields.






Mayowa –
I’m impressed with the educational value and practical applications covered in this digital service. The explanations of data collection methods, predictive modeling, and decision-support systems were clear and informative. The interactive tools and case studies helped us understand how to apply data analytics to our specific farming challenges. It’s empowered us to make informed decisions that enhance productivity and sustainability.
Labaran –
This digital service on data analytics for precision agriculture has transformed how we approach farming. The in-depth analysis of crop data, weather patterns, and soil conditions has provided us with actionable insights to optimize our operations. We’ve improved crop yields, reduced input costs, and minimized environmental impact. It’s an invaluable tool for any farmer committed to sustainable and data-driven agriculture.