Description
Comparing flood irrigation with other irrigation methods like drip and sprinkler systems highlights several key differences in terms of efficiency, application, and impact:
- Water Efficiency:
- Flood Irrigation: Typically has lower water use efficiency compared to drip and sprinkler systems due to greater losses from evaporation, runoff, and deep percolation.
- Drip Irrigation: Delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing losses and often achieving higher efficiency in water use.
- Sprinkler Irrigation: Uses overhead sprinklers to distribute water, with efficiency falling between flood and drip methods depending on design and management.
- Application Precision:
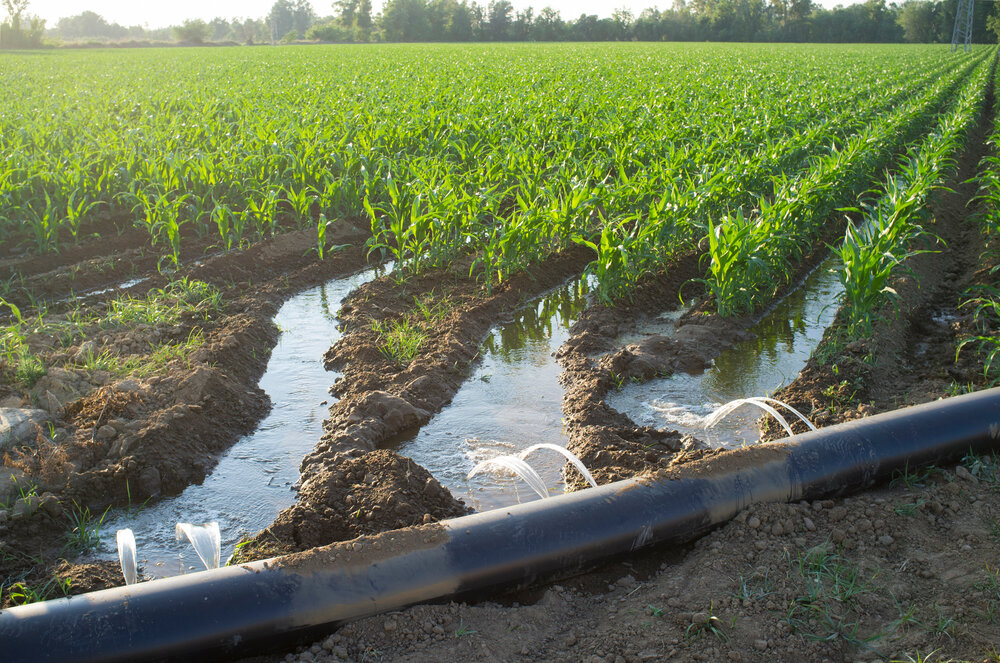
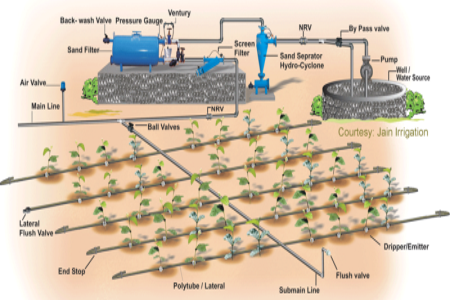
- Flood Irrigation: Applies water uniformly over large areas, but lacks precision in targeting specific plant roots, leading to potential water wastage.
- Drip Irrigation: Precisely delivers water to individual plants or along rows, minimizing water contact with foliage and reducing weed growth.
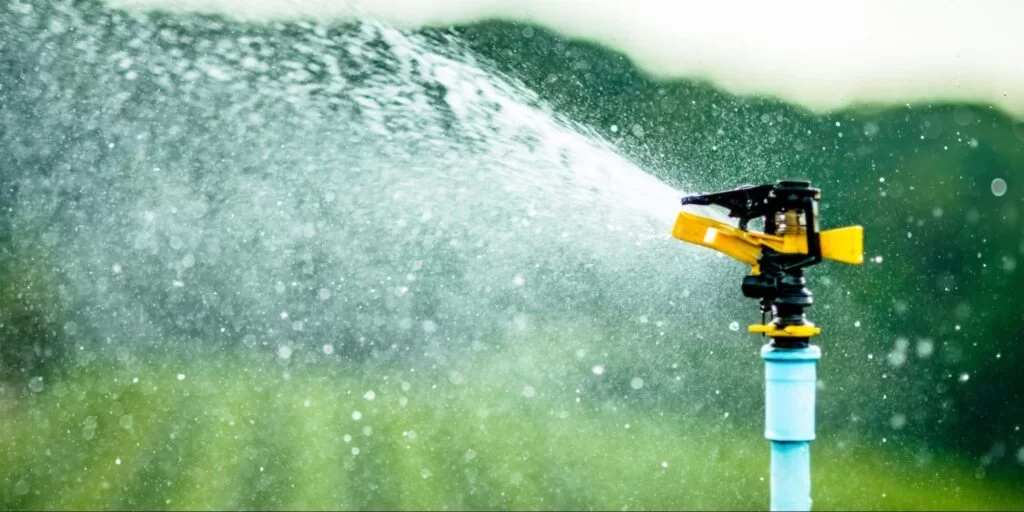
- Sprinkler Irrigation: Covers larger areas than drip systems but may lead to water loss due to wind drift and evaporation.
- Labor and Management:
- Flood Irrigation: Requires significant labor for water distribution and management of channels or ditches.
- Drip Irrigation: Initially requires more labor for installation but reduces ongoing labor needs for operation and maintenance compared to flood systems.
- Sprinkler Irrigation: Falls between flood and drip methods in terms of labor requirements, depending on system complexity and size.
- Crop Suitability:
- Flood Irrigation: Suitable for a wide range of crops, particularly those tolerant of wet conditions or where soil structure allows uniform water distribution.
- Drip Irrigation: Ideal for row crops, orchards, and gardens where precise water application is crucial for crop health and yield.
- Sprinkler Irrigation: Versatile for most crop types but may require adjustments for crops sensitive to water on foliage.
- Environmental Impact:
- Flood Irrigation Can contribute to soil erosion, nutrient runoff, and waterlogging, which can impact soil health and water quality.
- Drip Irrigation: Minimizes soil erosion and runoff, conserves water, and reduces fertilizer leaching.
- Sprinkler Irrigation: Moderates environmental impact depending on management practices and water application uniformity.
- Cost Considerations:
- Flood Irrigation: Initial setup costs are generally lower than drip or sprinkler systems, but ongoing operational costs can be higher due to water usage inefficiencies.
- Drip Irrigation: Higher initial investment but potential long-term savings through reduced water and labor costs.
- Sprinkler Irrigation: has moderate initial and operational costs, and depending on setup and management, it can be balanced between flood and drip systems.






Olamide –
We’ve found the comparative analysis of flood irrigation methods from this digital service to be both effective and insightful. The comprehensive evaluations and performance metrics helped us implement strategic changes in our irrigation practices. The ongoing support and updates have kept us informed of industry trends and innovations. It’s a valuable investment for anyone seeking to optimize irrigation efficiency and minimize resource use.
Tijani –
This digital service goes beyond traditional flood irrigation discussions to explore sustainable farming practices. The emphasis on water conservation and soil health resonates deeply with our farm’s values. The comparative analysis provided clarity on which methods align best with our goals of reducing environmental impact while maintaining productivity. Highly recommend for progressive farmers committed to sustainability.
Ronke –
I’m impressed with the depth of knowledge and practical advice provided by this digital service. The comparative analysis not only highlighted the pros and cons of different flood irrigation methods but also offered actionable recommendations for improvement. The interactive charts and case studies were particularly enlightening. It’s been instrumental in guiding our decision-making process and achieving better outcomes in our fields.
Haladu –
This comparative analysis of flood irrigation methods has been invaluable for optimizing water usage on our farm. The detailed comparisons and data-driven approach helped us identify the most efficient techniques for our crops. We’ve already seen a significant reduction in water waste and improved crop yields. It’s a must-have resource for any farmer looking to enhance sustainability practices.