Description
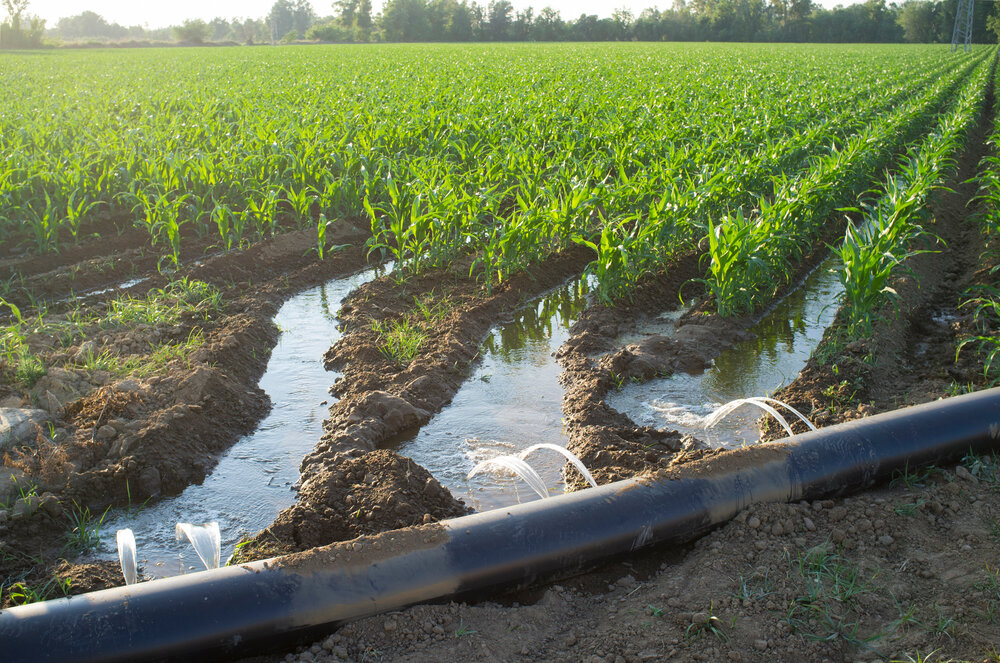
Flood irrigation is a traditional method of watering crops or fields where water is applied to the entire field surface, allowing it to soak into the soil. Here’s an overview of flood irrigation:
- Method: Water is released from ditches, pipes, or gated structures and flows over the land surface, uniformly covering the entire field.
- Types:
- Surface Irrigation: Water flows over the soil surface and infiltrates downwards.
- Furrow Irrigation: Water is directed into furrows (small trenches) between rows of crops.
- Basin Irrigation: Water is contained within small basins around individual plants or groups of plants.
- Advantages:
- Low Cost: Requires minimal infrastructure beyond simple channels or pipes.
- Suitable for Many Crops: Can be used for a wide range of crops and field types.
- Soil Improvement: The deposition of sediments and organic matter can contribute to soil fertility.
- Disadvantages:
- Water Loss: This can lead to significant water loss due to evaporation, runoff, and deep percolation.
- Labor Intensive: Requires careful management and labor for water distribution.
- Uniformity: Achieving uniform water distribution isn’t easy, leading to potential over- or under-watering of plants.
- Management Considerations:
- Water Application: The timing and amount of water must be carefully managed to avoid waterlogging or drought stress.
- Soil Type: Soil texture and structure affect water infiltration and distribution.
- Environmental Impact: Potential for soil erosion and nutrient runoff.






Odunayo –
This digital service not only introduced me to flood irrigation techniques but also emphasized their role in sustainable farming practices. The focus on water conservation and soil health resonated with my values as a farmer. The interactive quizzes and assessments helped reinforce my understanding of flood irrigation principles. I now feel equipped to implement these techniques responsibly and efficiently.
Muntari –
I found this introduction to flood irrigation incredibly educational and accessible. The digital platform’s user-friendly interface made it easy to navigate through the modules and absorb the information at my own pace. The real-life examples and case studies provided context and inspiration for applying flood irrigation techniques effectively. I feel empowered to make informed decisions that will benefit both my crops and the environment.
Mamuda –
This digital service provided an excellent introduction to flood irrigation, covering all the basics in a clear and concise manner. As someone new to farming, I appreciated the step-by-step guidance and practical tips for implementing flood irrigation on my property. The interactive elements and visuals made learning enjoyable and engaging. It’s been a valuable resource as I begin my journey into sustainable agriculture.