Description
Implementing rainwater harvesting systems in agriculture involves several steps to capture, store, and use rainwater efficiently. Here’s a comprehensive guide to setting up an effective rainwater harvesting system:
1. Assess Water Needs and Site Conditions
- Evaluate Water Requirements: Determine the amount of water needed for your crops or livestock.
- Analyze Site Conditions: Assess the topography, soil type, and rainfall patterns to plan the system effectively.
2. Design the System
- Catchment Area: Identify and prepare the catchment area, typically rooftops or open fields, where rainwater will be collected.
- Conveyance System: Install gutters, downspouts, and pipes to direct rainwater from the catchment area to the storage tank.
- Storage Tanks: Select appropriate storage tanks (e.g., plastic, concrete, or metal) based on water needs and available space. Ensure tanks are covered to prevent contamination and evaporation.
- Filtration System: Implement a filtration system to remove debris and contaminants before storing water. This can include mesh filters, first-flush diverters, and sedimentation tanks.
3. Installation
- Gutters and Downspouts: Install gutters along the edges of rooftops and connect them to downspouts.
- Piping System: Lay pipes to convey water from downspouts to storage tanks. Ensure pipes are properly sloped for efficient water flow.
- Storage Tanks: Place storage tanks on stable, level ground. Connect pipes to the tanks and install inlet filters.
- Overflow System: Design an overflow system to manage excess water during heavy rains, directing it to secondary storage or safe drainage areas.
4. Maintenance
- Regular Cleaning: Clean gutters, downspouts, and filters regularly to prevent clogging and contamination.
- Tank Maintenance: Inspect and clean storage tanks periodically to remove sediment and algae.
- System Checks: Perform routine checks on the entire system, including pipes, valves, and seals, to ensure proper functioning.
5. Usage and Management
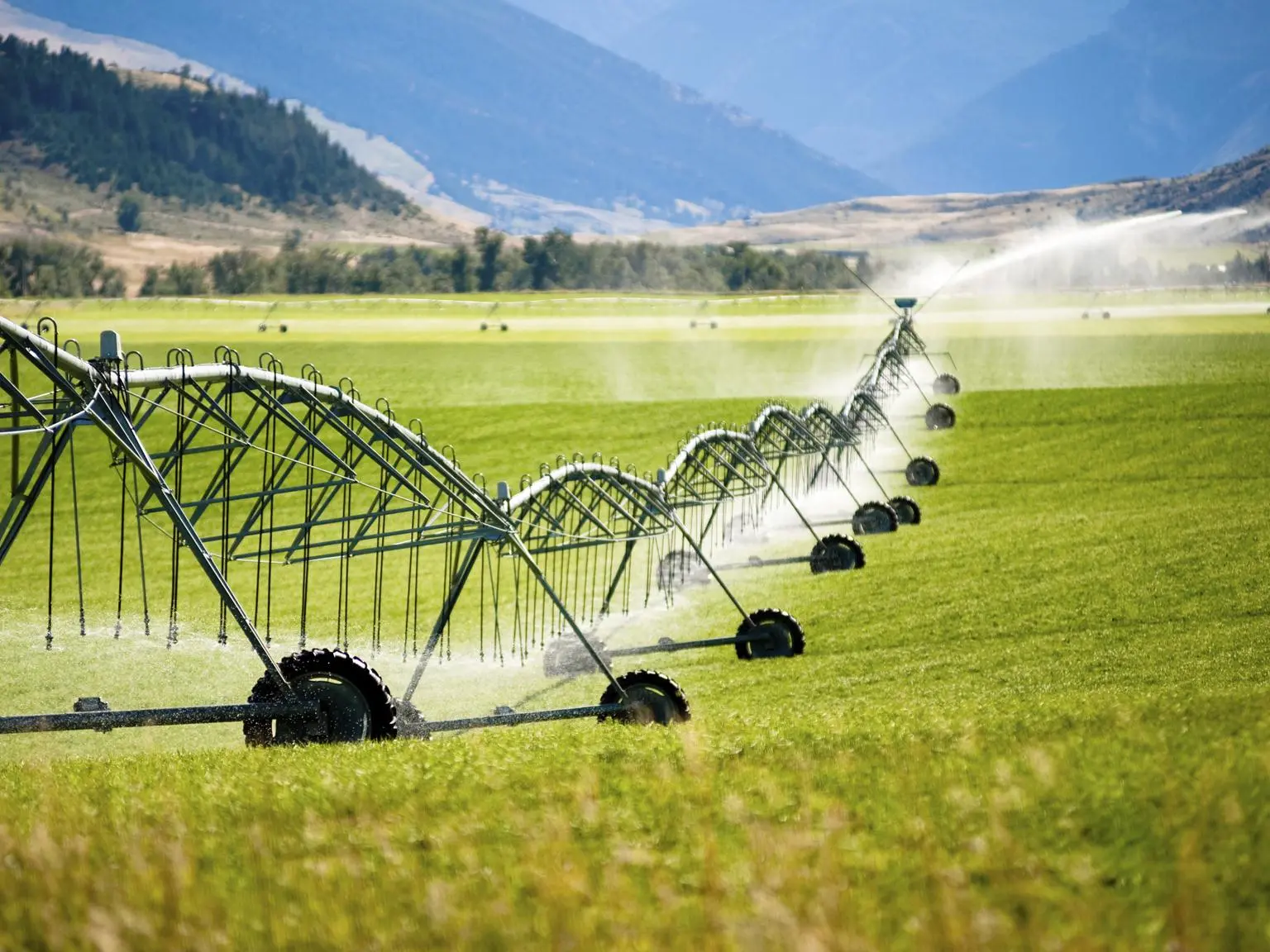
- Irrigation Integration: Connect the harvested rainwater system to your irrigation system. Use pumps if necessary to distribute water efficiently.
- Water Management: Monitor water levels and usage to optimize water distribution and prevent wastage.
- Drought Management: Use stored rainwater strategically during dry periods to maintain crop health.
6. Benefits and Considerations
- Cost Savings: Reduces dependency on municipal or well water, leading to cost savings.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces runoff, erosion, and pressure on local water sources.
- Sustainability: Promotes sustainable water use and enhances resilience to climate variability.
7. Legal and Community Aspects
- Permits and Regulations: Check local regulations and obtain necessary permits for rainwater harvesting.
- Community Engagement: Educate and involve the local community in rainwater harvesting practices to promote widespread adoption.


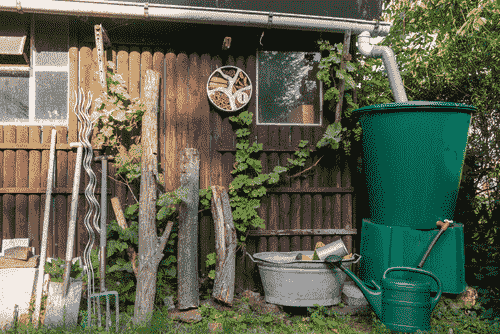





Adedayo –
This digital service on implementing rainwater harvesting systems has been a game-changer for our farm. The practical advice and step-by-step guides helped us design and install a rainwater collection system tailored to our needs. We’ve significantly reduced our reliance on municipal water sources and have seen improvements in soil moisture and crop health. It’s an essential resource for any farmer committed to sustainable water management.
Tawakalitu –
This digital service on implementing rainwater harvesting systems has been a game-changer for our farm. The practical advice and step-by-step guides helped us design and install a rainwater collection system tailored to our needs. We’ve significantly reduced our reliance on municipal water sources and have seen improvements in soil moisture and crop health. It’s an essential resource for any farmer committed to sustainable water management.