Description
Water-efficient landscaping, also known as xeriscaping, involves designing and maintaining landscapes to minimize water use while maintaining aesthetics and functionality. Here are key practices to achieve water-efficient landscaping:
1. Planning and Design
- Site Analysis: Assess the site’s soil type, sun exposure, slope, and existing vegetation to plan a water-efficient landscape.
- Zoning: Group plants with similar water needs together to ensure efficient irrigation.
- Functional Areas: Designate areas for specific uses (e.g., play areas, seating, garden beds) to concentrate watering efforts where most needed.
2. Soil Improvement
- Soil Testing: Test soil to determine its structure, pH, and nutrient content.
- Amendments: Incorporate organic matter, such as compost, to improve soil water-holding capacity and fertility.
- Mulching: Apply mulch to reduce evaporation, maintain soil temperature, and suppress weeds.
3. Plant Selection
- Native Plants: Choose native plants that are adapted to local climate and soil conditions, requiring less water and maintenance.
- Drought-Tolerant Plants: Select drought-tolerant species that can thrive with minimal water.
- Plant Diversity: Use a variety of plants to create a resilient and attractive landscape that can better withstand drought.
4. Efficient Irrigation
- Drip Irrigation: Install drip irrigation systems to deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
- Smart Controllers: Use smart irrigation controllers that adjust watering schedules based on weather conditions and soil moisture levels.
- Rain Sensors: Install rain sensors to automatically shut off irrigation systems during rainfall.
- Watering Schedule: Water early in the morning or late in the evening to reduce evaporation losses.
5. Lawn Alternatives
- Reduce Lawn Area: Replace traditional lawns with ground covers, native grasses, or hardscaping to reduce water use.
- Drought-Resistant Grass: If maintaining a lawn, choose drought-resistant grass varieties that require less water.
6. Mulching
- Organic Mulch: Use organic mulches such as bark, wood chips, or straw to retain soil moisture and improve soil health.
- Inorganic Mulch: Consider inorganic options like gravel or stone for areas where organic mulch might not be suitable.
7. Maintenance Practices
- Weed Control: Regularly remove weeds that compete with plants for water.
- Pruning: Prune plants appropriately to reduce water demand and promote healthy growth.
- Mowing: Mow lawns at the highest recommended height to encourage deep root growth and shade the soil.
8. Rainwater Harvesting
- Rain Barrels: Install rain barrels to collect and store rainwater for irrigation.
- Rain Gardens: Create rain gardens to capture and infiltrate rainwater, reducing runoff and promoting groundwater recharge.
9. Hardscaping
- Permeable Surfaces: Use permeable materials for walkways and patios to allow water infiltration and reduce runoff.
- Efficient Design: Incorporate features like gravel paths, stone patios, and retaining walls to reduce the need for irrigated areas.
10. Landscape Maintenance
- Regular Inspections: Check irrigation systems for leaks, clogs, and inefficiencies.
- Seasonal Adjustments: Adjust irrigation schedules seasonally based on plant needs and weather conditions.
- Water-Wise Practices: Encourage deep, infrequent watering to promote deep root growth and drought tolerance.
11. Education and Community Involvement
- Workshops and Seminars: Participate in or organize workshops to learn about water-efficient landscaping techniques.
- Community Projects: Engage in community projects to promote and implement water-efficient landscaping in public spaces.




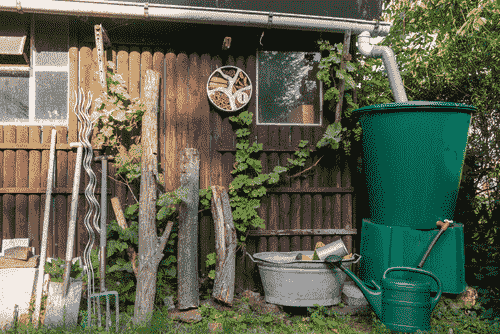



Ifeyinwa –
The practical advice and actionable strategies from this digital service have exceeded our expectations. We’ve implemented several water-saving techniques based on the guidance provided and have already seen significant savings on our water bill. The digital platform’s user-friendly interface allowed us to explore different landscaping ideas and choose solutions that fit our budget and aesthetic preferences. It’s been a worthwhile investment in our home’s sustainability.
Balarabe –
This digital service aligns perfectly with our commitment to sustainable living and environmental stewardship. The emphasis on drought-tolerant plants and rainwater harvesting techniques resonates with our values. The personalized recommendations and step-by-step guides tailored to our specific landscape challenges have been invaluable. We now have a thriving garden that conserves water and supports local biodiversity. It’s a must-have resource for anyone interested in creating a sustainable outdoor oasis.
Kasimu –
I’m impressed with the educational value provided by this digital service. The comprehensive coverage of water-efficient landscaping, from native plant selection to smart irrigation strategies, was enlightening. The interactive tools and design templates made it easy to plan and implement sustainable practices on our property. We’ve been able to enhance curb appeal while minimizing our environmental footprint. Highly recommend for homeowners and landscapers alike.
Ogbonna –
This digital service on water-efficient landscaping practices has been a game-changer for our property. The practical advice and innovative techniques helped us create a beautiful landscape while significantly reducing water usage. We’ve seen improvements in plant health and soil moisture retention, even during drought conditions. It’s an essential resource for anyone looking to create an eco-friendly and sustainable outdoor environment.